在高校学生组织管理领域,传统的人工操作模式面临着信息孤岛、流程繁琐、数据统计困难等系统性挑战。针对这一痛点,我们设计并实现了一套基于SSH框架的校园社团智能管理平台,通过数字化手段重构社团管理全流程,为高校学生工作提供标准化、可扩展的技术解决方案。
系统架构与技术栈设计
该平台采用经典的三层架构模式,每一层都选用成熟稳定的技术框架确保系统的可靠性和可维护性。
表现层使用Struts2框架处理用户请求与响应,通过精心设计的Action类实现前后端数据交互。Struts2的拦截器机制为系统提供了统一的权限验证和日志记录能力。
public class UserAction extends ActionSupport {
private UserService userService;
private List<User> userList;
private User user;
// 用户登录验证
public String login() {
User currentUser = userService.validateLogin(user.getXuehao(), user.getLoginpw());
if (currentUser != null) {
ActionContext.getContext().getSession().put("currentUser", currentUser);
return SUCCESS;
}
return ERROR;
}
// 获取用户列表
public String list() {
userList = userService.findAllUsers();
return SUCCESS;
}
}
业务逻辑层基于Spring框架构建,利用控制反转(IoC)和依赖注入(DI)实现组件解耦。通过面向切面编程(AOP)统一管理事务边界,确保数据操作的原子性和一致性。
<!-- Spring Bean配置 -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.club.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理配置 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
数据持久层采用Hibernate ORM框架,通过对象关系映射将Java实体类与数据库表结构建立对应关系,简化了数据访问操作。HQL查询语言提供了面向对象的查询方式,提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements UserDao {
public User findByXuehao(String xuehao) {
String hql = "from User where xuehao = ? and del = 'no'";
List<User> list = this.getHibernateTemplate().find(hql, xuehao);
return list.isEmpty() ? null : list.get(0);
}
public List<User> findActiveUsers() {
String hql = "from User where del = 'no' order by xuehao";
return this.getHibernateTemplate().find(hql);
}
}
数据库设计深度解析
数据库设计是系统稳定性的基石,通过对核心表结构的优化设计,确保了数据的一致性和查询效率。
申请流程表(t_shenqing)设计分析
申请表的设计体现了业务流程的完整性追踪需求。每个申请记录包含完整的生命周期信息,从提交申请到审核回复的全过程都有详细记录。
CREATE TABLE `t_shenqing` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '申请ID',
`shetuan_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '社团ID',
`user_id` int(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`liyou` varchar(2000) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '理由',
`shenqingshi` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '申请时间',
`huifuxinxi` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '回复信息',
`huifushi` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '回复时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='申请表'
设计亮点:
liyou字段采用varchar(2000)类型,充分考虑了申请理由的文字长度需求- 时间字段统一使用varchar类型存储格式化后的时间字符串,便于前端展示
- 通过
shetuan_id和user_id建立与社团表和用户表的关联关系 - 缺乏外键约束的设计选择提高了系统灵活性,但需要在应用层保证数据一致性
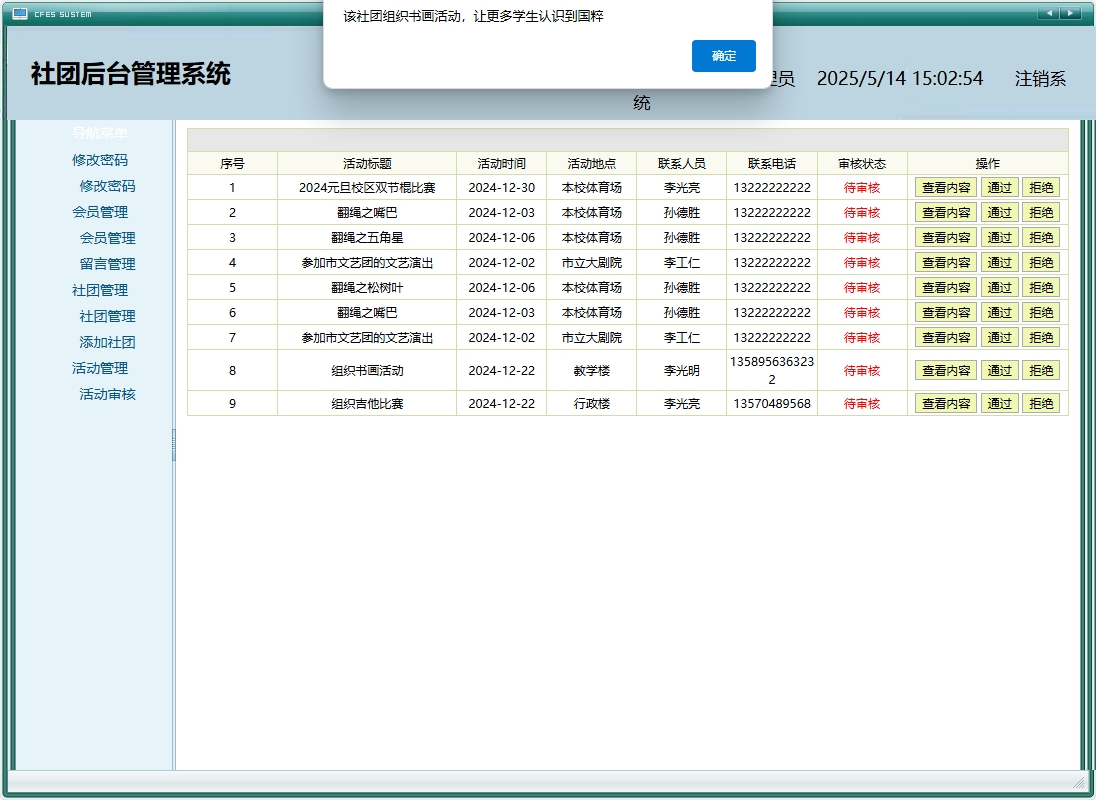
活动管理表(t_huodong)的业务逻辑体现
活动表的设计充分考虑了校园活动的实际管理需求,包含了活动的基本信息、状态管理和审核流程。
CREATE TABLE `t_huodong` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '活动ID',
`shetuan_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '社团ID',
`biaoti` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '标题',
`neirong` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '内容',
`shijian` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '时间',
`didian` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '地点',
`lianxiren` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人',
`lianxihua` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系话',
`status` int(2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '状态',
`shenheren` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '审核人',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=27 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='活动表'
状态字段设计:status字段采用整型数值表示不同的审核状态(如:0-待审核,1-已通过,2-已拒绝),这种设计便于扩展新的状态类型,同时提高了查询效率。
核心功能实现详解
社团成员申请与审核流程
系统实现了完整的成员申请-审核工作流,学生可以提交加入社团的申请,社团负责人进行审核并反馈结果。
public class ShenqingAction extends ActionSupport {
private ShenqingService shenqingService;
private Shenqing shenqing;
// 提交社团申请
public String submitApplication() {
User currentUser = (User) ActionContext.getContext().getSession().get("currentUser");
shenqing.setUser_id(currentUser.getId());
shenqing.setShenqingshi(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
shenqingService.saveApplication(shenqing);
return SUCCESS;
}
// 审核申请
public String reviewApplication() {
shenqing.setHuifushi(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
shenqingService.updateApplication(shenqing);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
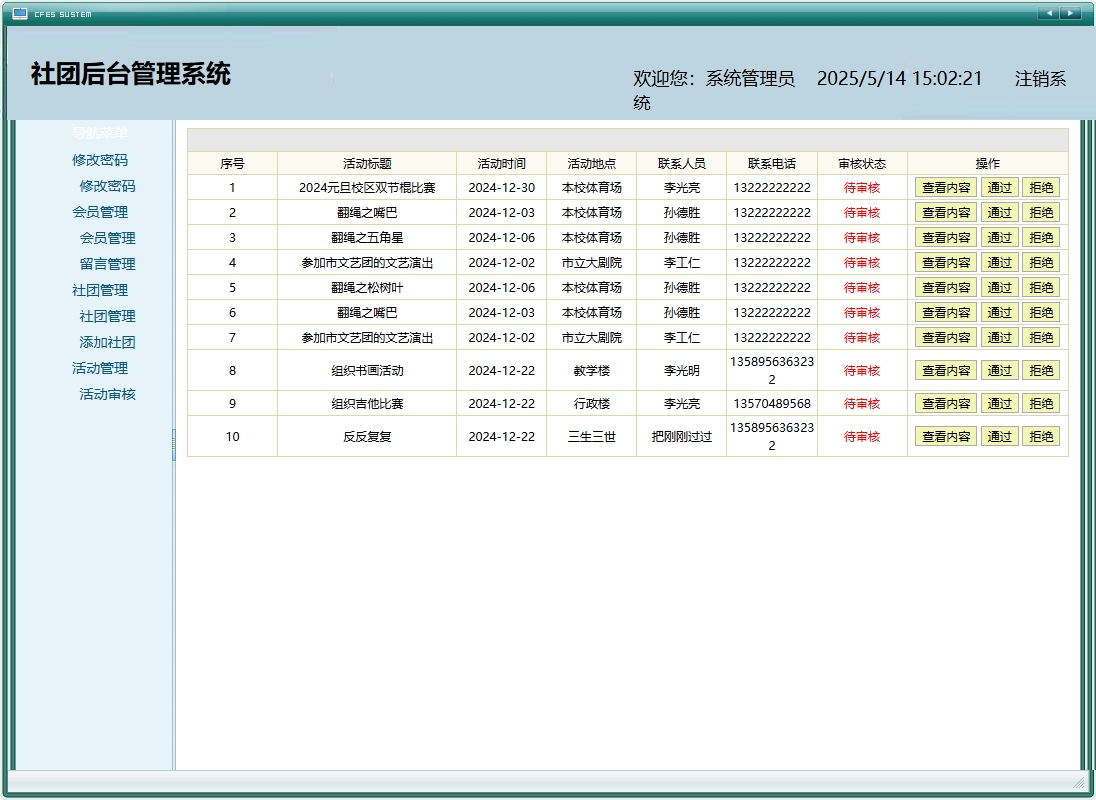
活动发布与管理系统
活动管理模块支持社团负责人创建活动、设置活动详情,并需要经过管理员审核才能正式发布。
public class HuodongService {
public void createActivity(Huodong activity) {
// 设置初始状态为待审核
activity.setStatus(0);
activity.setShijian(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm").format(new Date()));
huodongDao.save(activity);
}
public List<Huodong> getApprovedActivities() {
String hql = "from Huodong where status = 1 order by shijian desc";
return huodongDao.find(hql);
}
public void approveActivity(int activityId, String auditor) {
Huodong activity = huodongDao.findById(activityId);
activity.setStatus(1);
activity.setShenheren(auditor);
huodongDao.update(activity);
}
}
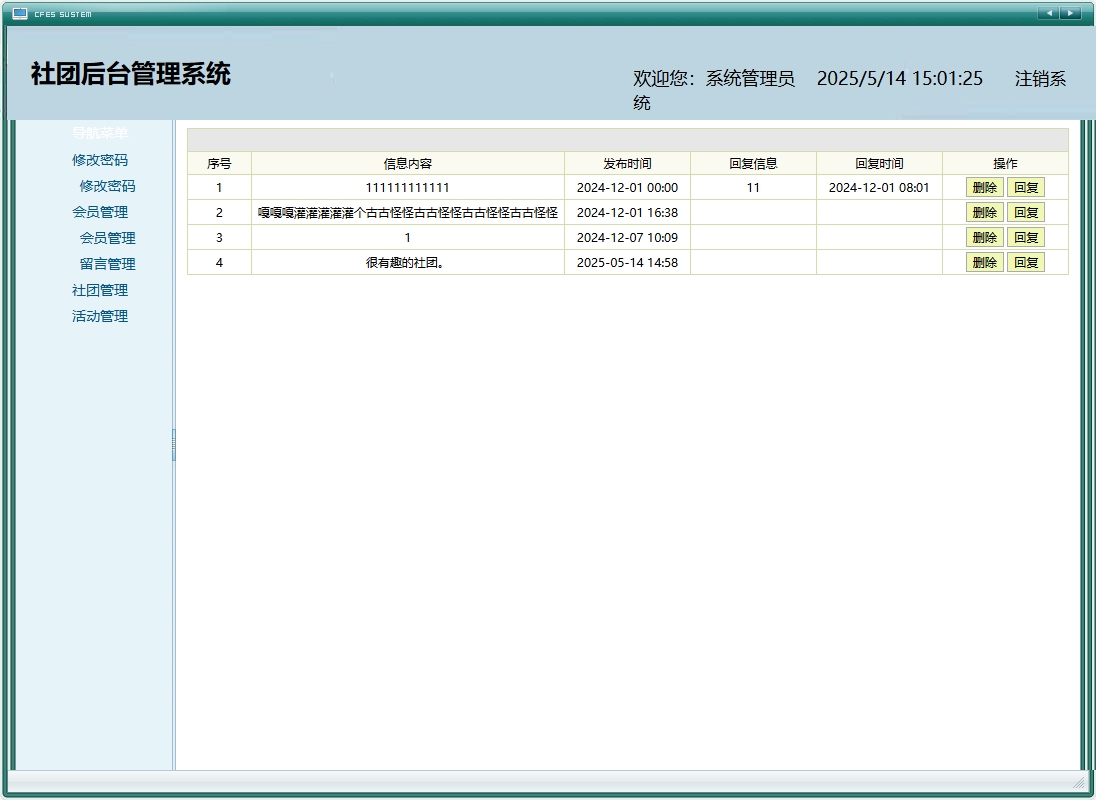
留言板与互动交流功能
留言板功能为社团成员提供了交流平台,支持留言、回复等互动操作,增强了社团内部的沟通效率。
public class LiuyanAction extends ActionSupport {
public String addMessage() {
User user = (User) ActionContext.getContext().getSession().get("currentUser");
liuyan.setUserId(user.getId());
liuyan.setLiuyanshi(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
liuyanService.saveMessage(liuyan);
return SUCCESS;
}
public String replyMessage() {
liuyan.setHuifushi(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
liuyanService.updateMessage(liuyan);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
用户权限与安全管理
系统采用基于角色的权限控制机制,不同角色的用户拥有不同的操作权限,确保数据安全性。
public class SecurityInterceptor implements Interceptor {
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
ActionContext context = invocation.getInvocationContext();
Map<String, Object> session = context.getSession();
User user = (User) session.get("currentUser");
if (user == null) {
return "login"; // 跳转到登录页面
}
// 检查权限
String actionName = invocation.getProxy().getActionName();
if (!hasPermission(user, actionName)) {
return "noPermission";
}
return invocation.invoke();
}
}
实体模型设计与领域建模
系统采用面向对象的领域模型设计,每个实体类都对应数据库中的一张表,通过Hibernate映射实现对象持久化。
用户实体模型
@Entity
@Table(name = "t_user")
public class User {
@Id
private Integer id;
private String xuehao; // 学号
private String xingming; // 姓名
private String xingbie; // 性别
private String nianling; // 年龄
private String banji; // 班级
private String loginpw; // 登录密码
private String del; // 删除标记
// 关联关系
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "user")
private Set<Shenqing> shenqingSet = new HashSet<>();
// getter和setter方法
public String getXuehao() { return xuehao; }
public void setXuehao(String xuehao) { this.xuehao = xuehao; }
// 其他getter/setter方法...
}
社团活动实体模型
@Entity
@Table(name = "t_huodong")
public class Huodong {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private Integer shetuan_id; // 社团ID
private String biaoti; // 标题
private String neirong; // 内容
private String shijian; // 时间
private String didian; // 地点
private String lianxiren; // 联系人
private String lianxihua; // 联系电话
private Integer status; // 状态
private String shenheren; // 审核人
// 业务逻辑方法
public boolean isApproved() {
return status != null && status == 1;
}
public boolean isPending() {
return status != null && status == 0;
}
}
功能展望与系统优化方向
基于当前系统架构和业务需求,未来可以从以下几个方向进行深度优化和功能扩展:
1. 引入Redis缓存提升系统性能
当前系统在频繁查询操作(如活动列表、用户信息等)中存在性能瓶颈。通过引入Redis作为缓存层,可以显著提升系统响应速度。
@Service
public class CachedHuodongService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private static final String ACTIVITY_CACHE_KEY = "activities:approved";
public List<Huodong> getApprovedActivities() {
// 先查询缓存
List<Huodong> activities = (List<Huodong>) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(ACTIVITY_CACHE_KEY);
if (activities == null) {
// 缓存未命中,查询数据库
activities = huodongDao.findApprovedActivities();
// 写入缓存,设置过期时间
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(ACTIVITY_CACHE_KEY, activities, Duration.ofHours(1));
}
return activities;
}
}
2. 微服务架构改造
随着业务复杂度的增加,可以将单体应用拆分为多个微服务,如用户服务、活动服务、审批服务等,提高系统的可扩展性和可维护性。
# 微服务配置示例
spring:
application:
name: club-activity-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
# API网关路由配置
zuul:
routes:
user-service:
path: /user/**
serviceId: user-service
activity-service:
path: /activity/**
serviceId: activity-service
3. 移动端适配与PWA应用
开发响应式前端界面,并实现PWA(渐进式Web应用)特性,使系统在移动设备上具有原生应用般的用户体验。
// 服务工作者注册
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/sw.js')
.then(registration => {
console.log('SW registered: ', registration);
})
.catch(registrationError => {
console.log('SW registration failed: ', registrationError);
});
}
4. 大数据分析与可视化报表
集成数据分析组件,为学校管理层提供社团运营的数据洞察和可视化报表。
@Service
public class AnalyticsService {
public ClubStatistics generateClubStats(Integer clubId) {
// 统计社团活跃度、成员增长、活动频率等指标
ClubStatistics stats = new ClubStatistics();
stats.setMemberCount(memberDao.countByClub(clubId));
stats.setActivityCount(activityDao.countByClub(clubId));
stats.setAvgParticipation(participationDao.getAvgByClub(clubId));
return stats;
}
}
5. 消息队列实现异步处理
使用消息队列处理耗时操作(如邮件通知、数据导出等),提升系统吞吐量和用户体验。
@Component
public class NotificationService {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendApprovalNotification(ApprovalMessage message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("notificationExchange", "approval.email", message);
}
}
@Component
public class EmailConsumer {
@RabbitListener(queues = "emailQueue")
public void processEmail(ApprovalMessage message) {
// 异步发送邮件通知
emailService.sendApprovalResult(message);
}
}
总结
该校园社团智能管理平台通过SSH框架的有机整合,构建了一个功能完善、性能稳定的社团管理系统。系统在数据库设计上充分考虑了业务需求,在架构设计上体现了分层解耦的思想,在功能实现上覆盖了社团管理的核心业务流程。
通过对核心表结构的深度分析,可以看到设计者在数据一致性、查询性能和扩展性方面的深思熟虑。实体模型的设计体现了领域驱动设计的思想,将业务概念准确地映射为技术实现。
未来的优化方向显示了系统进一步发展的潜力,从性能优化到架构升级,从移动端适配到智能化分析,都为系统的持续演进提供了明确的技术路径。这种基于成熟技术栈、注重业务价值、预留扩展能力的系统设计方法,为同类校园管理系统的开发提供了有价值的参考范式。